More to Know About USB-C Connections - (USB-C Continued)

In our last breakdown of USB-C, we walked through the key features separating the USB-C connection type from its predecessors, focusing on the generations of USB technology and the upgrades offered by each of these cables.
As the standard across the board for charging and data transfer, it’s more important than ever to understand the specifics of the USB-C connection type, and its primary features. To review, a few of the most important elements of the USB-C connection type are:
Reversibility of the connector
Previous USB protocols such as USB 2.0 and 3.0 required a specific up or down orientation to connect properly. Now, USB-C connections work in either orientation meaning there is no true “right side up” Additionally, the USB-C cables now provide the same cable connector on either end, increasing the simplicity of connection.
Transfer Speeds & Power
Thunderbolt 3 and 4 connection types use the USB-C protocol and offer up to 40Gbps speeds. As a standard however, USB-C provides 10Gbps transfer speeds. The 24-pin cable is also capable of relaying more than just video and data, offering up to 100 watts of power allowing for charging high-powered devices beyond simple monitor extension and data transfer.

USB 2.0
480 Mbps

USB 3.2
Gen 1
5 Gbps

USB 3.2
Gen 2
10 Gbps

USB 3.2
Gen 2x2
20 Gbps

USB4
20 Gbps

USB4
40 Gbps

Thunderbolt™ 3
40 Gbps

Thunderbolt™ 4
40 Gbps
Form Factor & Common Connections
USB-C caters to devices with a smaller more compact form factor such as many modern laptops like Google’s Chromebooks and Apple’s new M1 Macs. Though USB-C is becoming more and more commonplace in connection with new technologies, not all devices require a USB-C cable. That said, smart phones, tablets, flash drives, SD card readers, power banks, external hard drives, and even some headphones are regularly using USB-C connections for their function.
Alternate Modes
With alternate modes, USB Type-C connector pins can carry other signals such as DisplayPort Alt Mode (often labeled DP Alt Mode) which provides the ability for DP laptops or tablets to connect directly to an external monitor via USB-C ports.
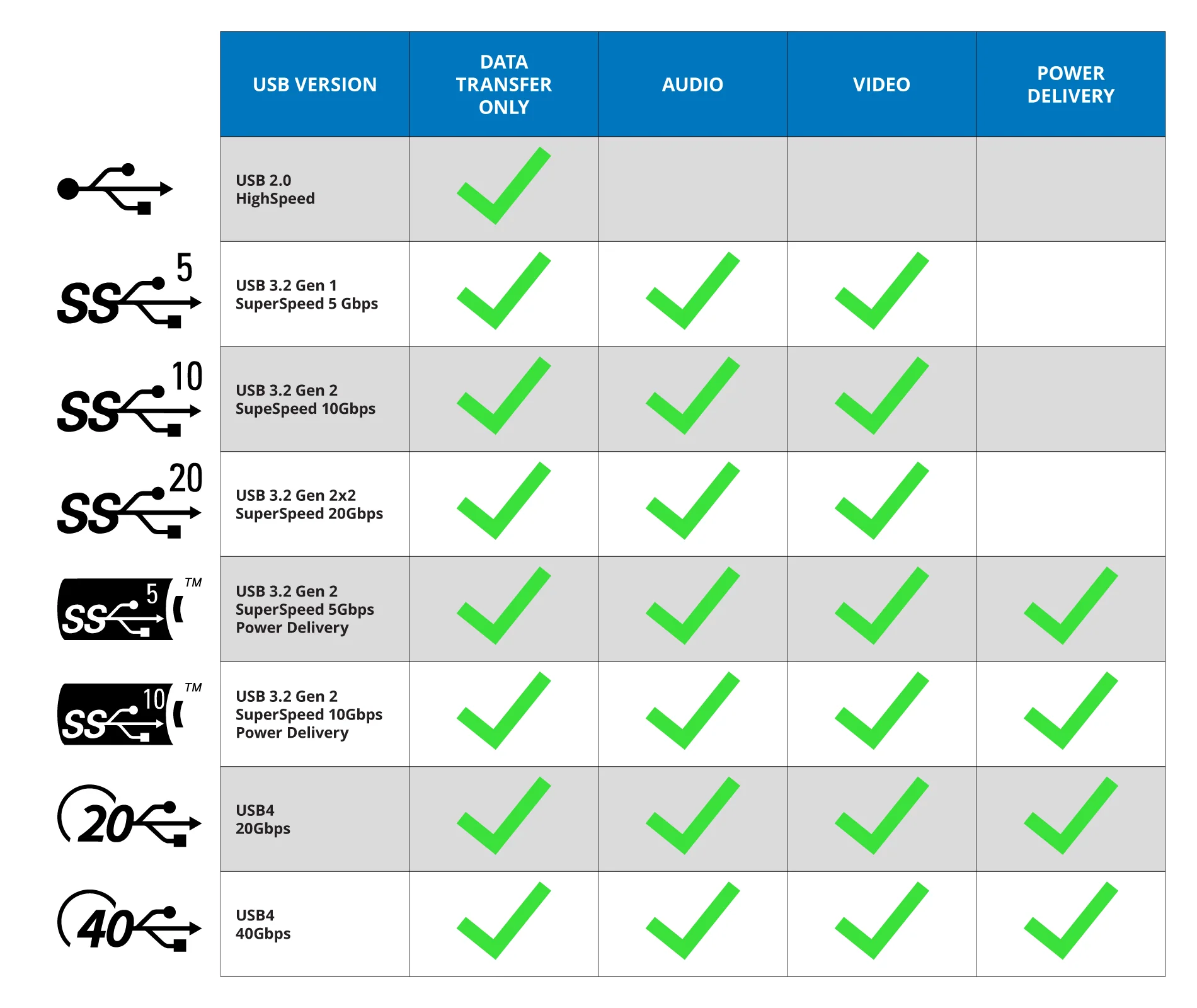
With each new generation of USB-C, we’ve seen different specifications that center around transfer speeds and compatibility. Here is a breakdown of USB-C transfer speeds:
Compatibility & Icons
USB-C supports USB4, 3.2, and 3.1 but is also backward compatible with both USB 3.0 and USB 2.0. See the USB Physical Compatibility Chart for details.
USB-C cables and adapters can help you connect to preferred monitor ports and attach to your favorite devices and peripherals. Check out VisionTek’s collection of USB-C cables and adapters here.
When will USB-C take over?
If you haven’t noticed it already, you’re sure to see it soon. Most modern laptops and desktops are putting USB-C ports on front panels and side connections alike. Being embraced by so many technology manufacturers across the board, it’s clear that USB-C is here to stay.
| USB Version | Also Known As | Connector Types | Max Transfer Speed | Max Cable Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB 1.1 | Full Speed USB | USB-A | 12 Mbps | 3 m |
| USB 2.0 | Hi-Speed USB | USB-A USB-C | 480 Mbps | 5 m |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 | USB 3.0 USB 3.1 Gen 1 SuperSpeed | USB-A USB-C | 5 Gbps | 3 m |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 | USB 3.1 USB 3.1 Gen 2 SuperSpeed+ Super Speed 10Gbps | USB-A USB-C | 10 Gbps | 3 m |
| USB 3.2 2x2 | USB 3.2 SuperSpeed 20Gbps | USB-C | 20 Gbps | 3 m |
| USB4 | USB4 Gen 2x2 USB4 20Gbps | USB-C | 20Gbps | .8 m |
| USB4 | USB4 Gen 3x2 USB4 40Gbps | USB-C | 40Gbps | .8 m |

